Denture In Chennai
A denture is a removable dental appliance that replaces missing teeth and the surrounding gum tissue. Dentures are custom-made to fit your mouth and restore both function (chewing, speaking) and appearance (smile, facial structure). Today’s dentures look more natural and fit more comfortably thanks to advancements in dental materials and digital impressions. Some patients also opt for implant-supported dentures, which are anchored to dental implants for added stability.
Dentures are a cost-effective and non-invasive solution for tooth loss, helping patients regain confidence and function in daily life. At Best Dental Clinic – Dr N Deenadayalan T Nagar, Chennai and Dr Julian’s Laser Dental Clinic, Tambaram Chennai, we provide professional denture services for all patients.
Key functions of Denture
-
Restore Chewing Ability: Enjoy proper eating and nutrition without discomfort
-
Improve Speech: Speak clearly and confidently.
-
Enhance Facial Aesthetics: Maintain a natural-looking smile and facial balance.
-
Support Lips and Cheeks: Prevent sagging and preserve facial contours.
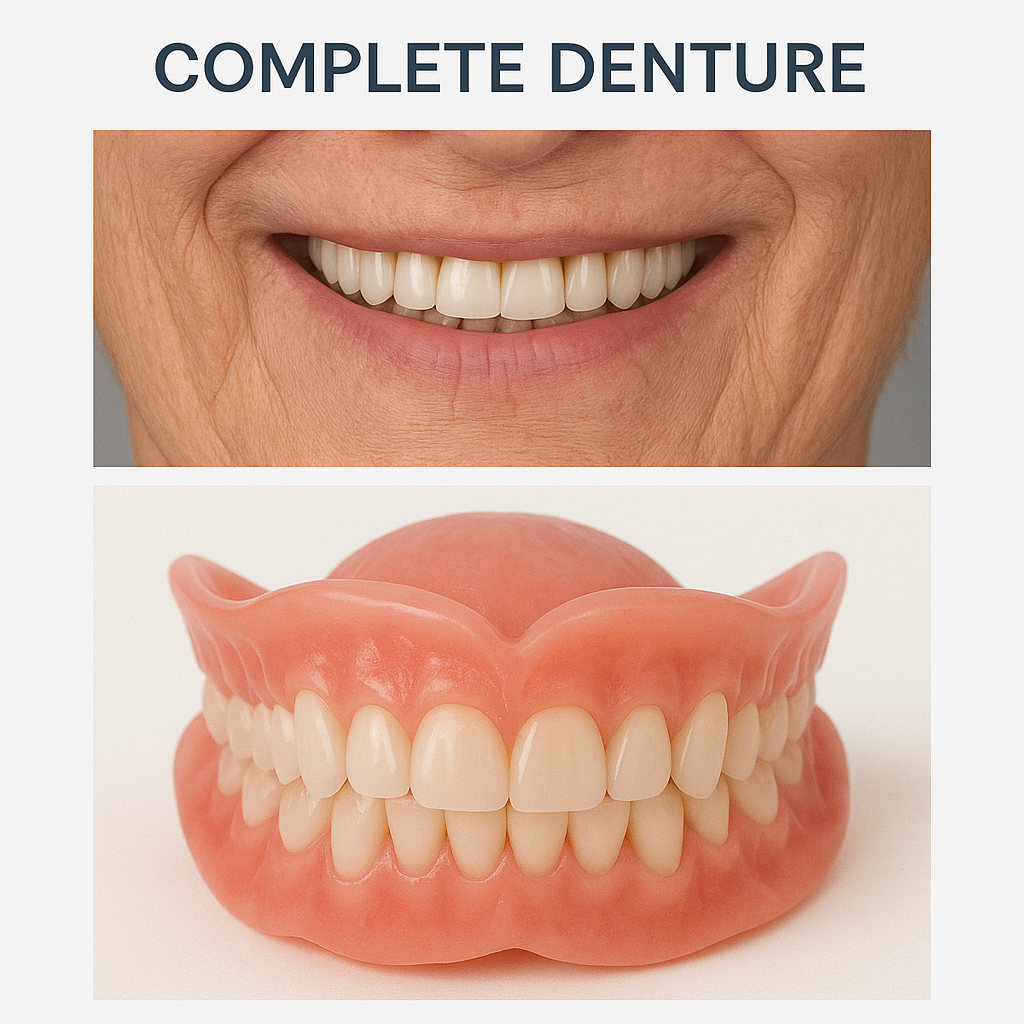
Complete Denture In Chennai
What is Complete Denture?
A complete denture is a removable dental appliance used to replace all missing teeth in either the upper or lower jaw, or both. It is typically recommended for individuals who have lost all their natural teeth due to age, gum disease, decay, or injury. At Best Dental Clinic – Dr N Deenadayalan T Nagar, Chennai and Dr Julian’s Laser Dental Clinic, Tambaram Chennai, we ensure complete dentures are custom-made for the best fit and comfort.
Complete dentures consist of a gum-colored acrylic base that fits snugly over the gums and a set of artificial teeth designed to look and function like natural ones.
There are two main types: conventional dentures, which are placed after the gums have healed following tooth extraction, and immediate dentures, which are inserted right after the teeth are removed, allowing the patient to have teeth during the healing process. While upper dentures often stay in place through suction, lower dentures may require adhesives or can be stabilized further with dental implants for a more secure fit.
Complete dentures help restore essential functions like chewing and speaking, support facial muscles to prevent a sunken appearance, and greatly improve the wearer’s confidence and quality of life. With proper care, regular cleaning, and occasional adjustments by a dentist, complete dentures can be a comfortable and long-lasting solution for full tooth loss.
Removable Partial Denture In Chennai
A removable partial denture (RPD) is a dental appliance designed to replace one or more missing teeth in a patient’s mouth when some natural teeth still remain. It consists of a gum-colored acrylic or metal base that supports artificial teeth, which are carefully crafted to match the size, shape, and color of the patient’s natural teeth. Best Dental Clinic – Dr N Deenadayalan T Nagar, Chennai and Dr Julian’s Laser Dental Clinic, Tambaram Chennai offer RPDs designed to preserve natural teeth while restoring function and aesthetics.
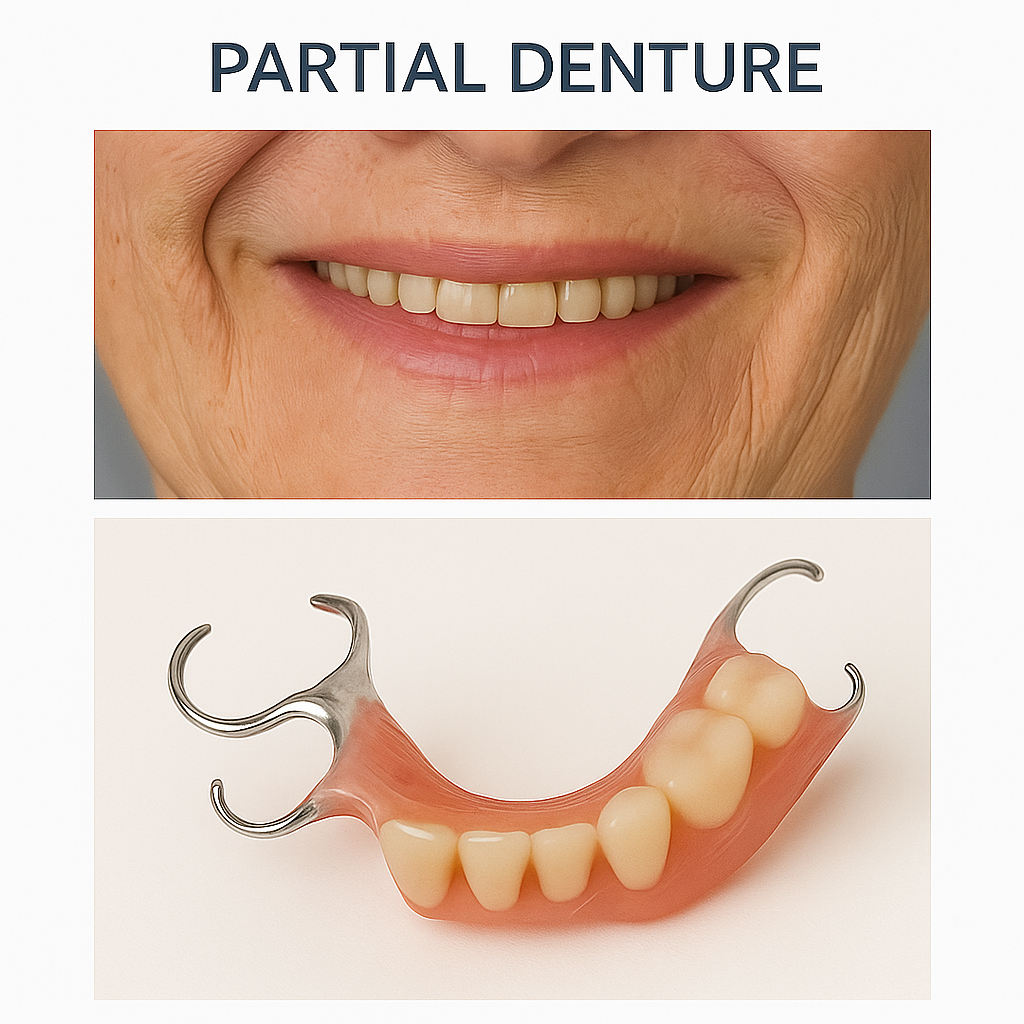
Partial dentures are designed to fit around the remaining natural teeth and are typically held in place using metal clasps, precision attachments, or flexible connectors, depending on the type and design.
They help restore proper chewing function, improve speech, and prevent the shifting of adjacent teeth, which can happen when gaps are left unfilled. Removable partial dentures are a cost-effective and less invasive option compared to dental implants or fixed bridges, and they can be taken out for cleaning and sleeping.
There are different types of RPDs—such as acrylic partials, metal framework partials, and flexible partials—each offering varying levels of comfort, strength, and aesthetics. With proper care and maintenance, including daily cleaning and regular dental check-ups, removable partial dentures can offer a functional and attractive solution for partial tooth loss while preserving the health of the remaining natural teeth.
RPD with Precision Attachments In Chennai
While standard removable partial dentures often use visible metal clasps to stay in place, a Removable Partial Denture (RPD) with Precision Attachments offers a much more aesthetic and stable alternative. This advanced dental appliance uses hidden “interlocking” components to secure the denture, providing a seamless look that mimics natural teeth.
A precision attachment is a two-part connector system: The Primary Part: A custom crown (cap) is placed over your remaining natural tooth, which contains a hidden “socket” or “slot”.The Secondary Part: The partial denture contains a matching “extension” or “key” that clicks perfectly into the socket of the crown.This “lock-and-key” mechanism eliminates the need for unsightly metal wires wrapped around your front teeth.
At Best Dental Clinic – Dr. N. Deenadayalan, T. Nagar and Dr. Julian’s Laser Dental Clinic, Tambaram, we specialize in these high-precision prosthetics to give our patients the ultimate combination of comfort, function, and discretion.
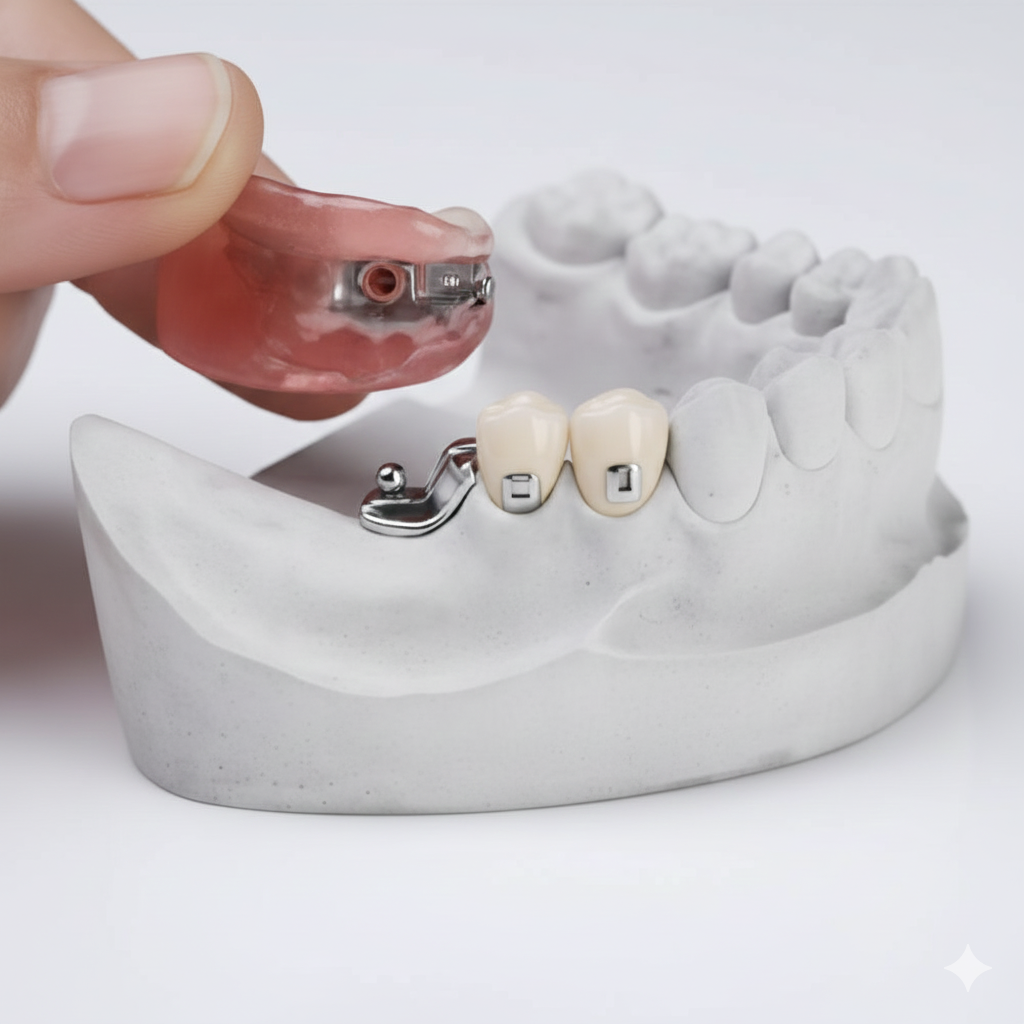
Benefits of Precision Attachment RPDs
-
Superior Aesthetics: Because the connectors are hidden inside the crowns and the denture, there are no visible metal clasps when you smile or speak.
-
Enhanced Stability: The mechanical interlocking provides a much tighter fit than standard partials, preventing the denture from slipping or clicking while eating.
-
Better Force Distribution: The design helps distribute chewing pressure more evenly across the remaining natural teeth and the jawbone, protecting your oral health.
-
Increased Comfort: These dentures are often less bulky than traditional RPDs, making them easier to wear throughout the day.
-
Bone Preservation: By providing a stable fit, they reduce the friction and irritation to the gums that can sometimes lead to bone loss.
Permanent Denture In Chennai
A permanent denture, also known as a fixed implant-supported bridge, is a long-term solution for patients missing most or all of their teeth. Unlike traditional dentures that rest on the gums and are removed daily, permanent dentures are securely anchored to the jawbone using dental implants. At Best Dental Clinic – Dr. N Deenadayalan T Nagar, Chennai and Dr. Julian’s Laser Dental Clinic, Tambaram Chennai, we use advanced implant technology to provide a smile that feels, looks, and functions exactly like natural teeth.
Permanent dentures are typically held in place by four to six implants per arch (commonly known as All-on-4 or All-on-6). Because they are fixed, they do not slip, click, or require messy adhesives, offering the highest level of stability and comfort available in modern restorative dentistry.
Benefits of Permanent Dentures
-
Unmatched Stability: Since they are screwed into implants, they never shift or fall out while eating or speaking.
-
Bone Preservation: The implants act as artificial tooth roots, stimulating the jawbone and preventing the facial sagging often caused by bone loss.
-
Natural Aesthetics: Designed with high-quality porcelain or zirconia, these dentures mimic the translucency and shape of natural teeth perfectly.
-
No Palate Covering: Unlike traditional upper dentures, permanent dentures do not cover the roof of your mouth, allowing you to taste food better and speak more naturally.
-
Convenience: There is no need to remove them at night or soak them in cleaning solutions. You brush them just like your natural teeth.
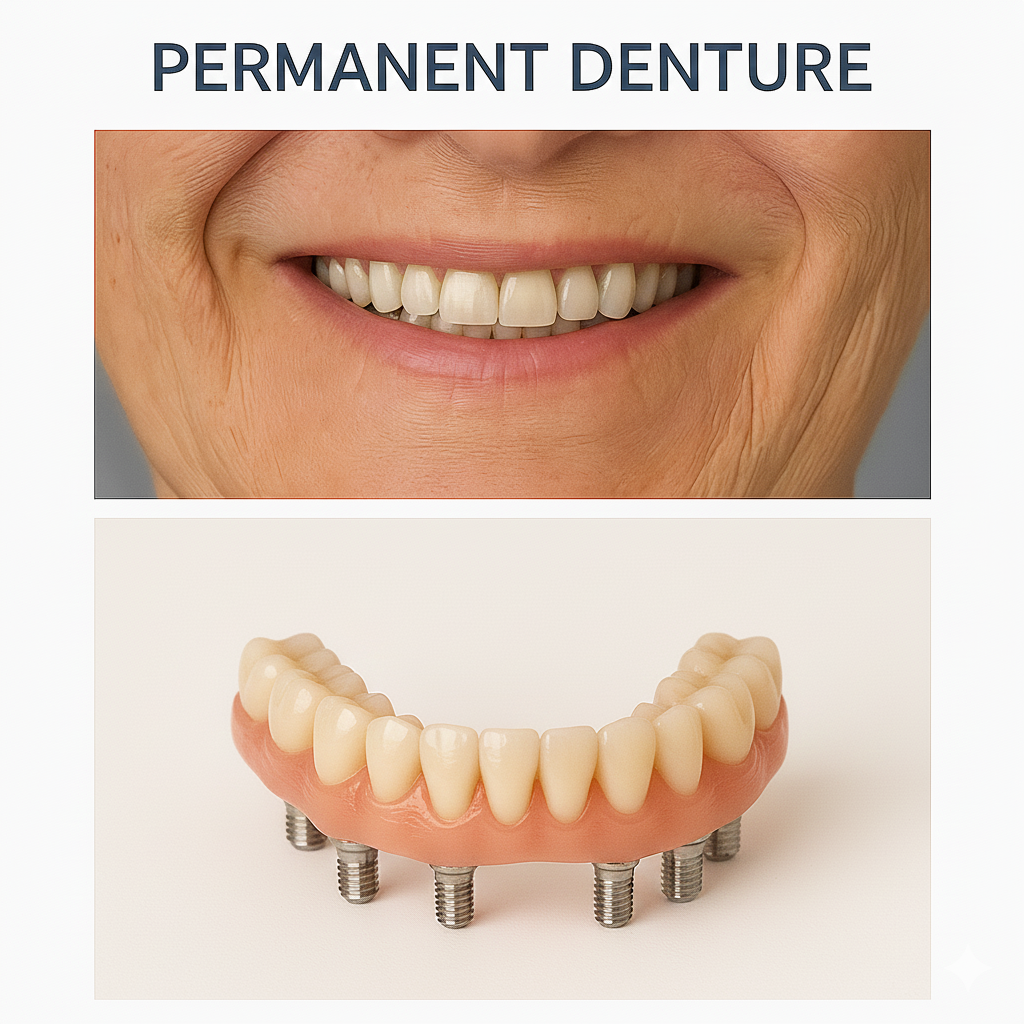
Is a Permanent Denture Right for You?
Permanent dentures are an ideal choice for patients who have sufficient bone density to support implants and are looking for a more “set-it-and-forget-it” solution. During your consultation at our Chennai clinics, we use digital imaging to assess your jaw health and create a customized treatment plan. Whether you are transitioning from removable dentures or dealing with failing teeth, permanent dentures can provide a life-changing improvement in your oral health and self-esteem.
Why Choose Us
At Best Dental Clinic – Dr N Deenadayalan T Nagar, Chennai and Dr Julian’s Laser Dental Clinic, Tambaram Chennai we are committed to delivering safe, advanced, and personalized dental care for every patient.
👩⚕️ Experienced Specialists
Our expert dentists and pediatric specialists ensure gentle, effective treatments for all ages
💎 Advanced Technology
We use modern equipment like dental lasers, digital X-rays, and advanced imaging for precise results.
🌟 Patient-Centered Care
We create a calm, friendly environment—especially for children—to make every visit stress-free.
🦷 Complete Dental Solutions
From cosmetic smile makeovers to child care and advanced surgeries, we cover all dental needs under one roof.
🏥 Trusted Clinics in Chennai
With two reputed branches in T Nagar and Tamabram, we are among the city’s most trusted dental care providers.
🔒 Safe & Hygienic Environment
We follow strict sterilization and hygiene protocols to ensure your complete safety during every procedure.
